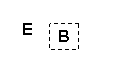Home | Levels > Tables | CQS | Rating | FAQ | Papers | Code | Blog | Calc (v3.Eng.Generic) | Calc (v3.Eng.FPS) |
13 different levels of functional consciousness are defined in ConsScale.
See below for a summary of the main features of each level.
Each level is characterized by architectural and behavioral criteria.
Table 1 covers architectural features and Table 2 behavioral profiles.
| Glossary | |
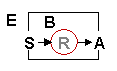
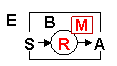
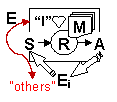
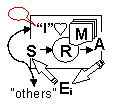
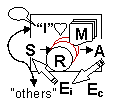
| E | Environment. World around the agent. |
| B | Body. Physical or simulated agent body. |
| Sext | Exteroceptive sensors. |
| Sproprio | Proprioceptive sensors. |
| A | Action Machinery. Agent effectors. |
| R | Reasoning. Sensorimotor coordination machinery. |
| M | Memory. Internal agent state. |
| Att | Attention mechanism to direct S and A to a specific Ei |
| Mn | Capability of multiple context representation. |
| SsA | Self-status assessment mechanism. |
| I | Mechanism for the representation of the self. |
| O | Mechanism for the representation of other selves. |
| AR | Accurate report mechanism. |
| AVR | Accurate verbal report mechanism. |
| Rn | Mechanism to run and synchronize several streams of consciousness. |
TABLE 1. ConsScale Levels of Consciousness (rev. 2.1)
|
|
|
Abstract Architecture |
Short Description |
|
|
|
|
Level -1 |
|
|
Boundaries
of the agent are not well defined. It can be confounded with the environment. |
None.
It is not a situated agent. |
Amino
acid as part of a protein. |
n/a |
|
Level 0 |
|
|
There
is an obvious distinction between body and environment, but no autonomous
processing. |
None.
It is not a situated agent. |
Isolated
chromosome. |
n/a |
|
Level 1 |
|
|
Presence
of sensors and/or actuators, but no relation between them. |
None.
It is not a situated agent. |
Dead
bacteria |
n/a |
|
Level 2 |
|
|
Fixed
reactive responses. R establishes an output of A
as a predetermined function of S. |
Primitive
situatedness based on reflexes. Evolutionary learning. |
Virus |
n/a |
|
Level 3 |
|
|
Actions
are a dynamic function of both memory and current information acquired by S. |
Basic
ability to learn and proprioceptive sensing allow orientation and positioning
behaviour. |
Earthworm |
1
Month. |
|
Level 4 |
|
|
Attention
mechanism selects Ei contents from S and M.
Emotions are present. |
Ability
to direct attention toward selected Ei allows attack and
escape behaviours. Directed learning. |
Fish |
5
Months. |
|
Level 5 |
|
|
Multiple
goals can be interleaved as they are explicitly represented in memory. |
Set
shifting capability allows multiple goal achievement. Basic emotional
learning. |
Quadruped
mammal |
9
Months. |
|
Level 6 |
|
|
Stable
and background emotions. Support for ToM stage 1: “I know”. |
Background
emotions provide a self-status assessment and influence behaviour. |
Monkey |
1
Year. |
|
Level 7 |
|
|
Support
for ToM stage 2: “I know I know”. |
Self-reference
makes possible advanced planning. Use of tools. |
Monkey |
1.5
Years. |
|
Level 8 |
|
|
Support
for ToM stage 3: “I know you know”. |
Making
of tools. Social behaviour. |
Chimpanzee |
2
Years. |
|
Level 9 |
|
|
Support
for ToM stage 4: “I know you know I know”. |
Accurate
report. Linguistic capabilities. Able to develop a culture. |
Human |
4
Years. |
|
Level 10 |
|
|
Human
like consciousness. Adapted Environment (Ec). |
Accurate
verbal report. Behaviour modulated by culture (Ec). |
Human |
Adult |
|
Level 11 |
|
|
Several
streams of consciousness in one self. |
Ability
to synchronize and coordinate several streams of consciousness. |
n/a |
n/a |
TABLE 2.
Cognitive Skills per Level.
|
Level |
Cognitive
Skills (CSi,j) |
|
2 |
CS2,1: Fixed reactive responses
(“reflexes”). |
|
3 |
CS3,1:
Autonomous acquisition of new adaptive reactive responses. CS3,2: Usage
of proprioceptive sensing for embodied adaptive responses. |
|
4 |
CS4,1: Selection of relevant sensory
information. CS4,2: Selection of relevant motor
information. CS4,3: Selection of relevant memory
information. CS4,4: Evaluation (positive or
negative) of selected objects or events. CS4,5: Selection of what needs to be
stored in memory. CS4,6: Trial and error learning.
Re-evaluation of selected objects or events. CS4,7: Directed behavior toward
specific targets like following or escape. CS4,8: Evaluation of the performance
in the achievement of a single goal. CS4,9: Basic planning capability:
calculation of next n sequential actions. CS4,10: Depictive representations of
percepts. |
|
5 |
CS5,1:
Ability to move back and forth between multiple tasks. CS5,2:
Seeking of multiple goals. CS5,3: Evaluation
of the performance in the achievement of multiple goals. CS5,4:
Autonomous reinforcement learning (emotional learning). CS5,5:
Advanced planning capability considering all active goals. |
|
6 |
CS6,1: Self-status
assessment (background emotions). CS6,2:
Background emotions cause effects in agent’s body. CS6,3:
Representation of the effect of emotions in organism (feelings). CS6,4:
Ability to hold a precise and updated map of body schema. CS6,5:
Abstract learning (learned lessons generalization). |
|
7 |
CS7,1: Representation of the
relation between self and perception. CS7,2: Representation of the
relation between self and action. CS7,3: Representation of the
relation between self and feelings. CS7,4: Self-recognition capability. CS7,5: Advance planning including
the self as an actor in the plans. CS7,6: Use of imaginational states
in planning. CS7,7: Learning of tool usage. |
|
8 |
CS8,1: Ability to model others as
subjective selves. CS8,2: Learning by imitation of a
counterpart. CS8,3: Ability to collaborate with
others in the pursuit of a common goal. CS8,4: Social planning (planning
with socially aware plans). CS8,5: Ability to make new tools. |
|
9 |
CS9,1: Ability to develop Machiavellian
strategies like lying and cunning. CS9,2: Social learning (learning of
new Machiavellian strategies). CS9,3: Advanced communication skills
(accurate report of mental content). CS9,4: Groups are able to develop a
culture. |
|
10 |
CS10,1: Accurate verbal report.
Advanced linguistic capabilities. CS10,2: Ability to pass the Turing
test. CS10,3: Ability to modify and adapt
the environment to agent’s needs. CS10,4: Groups are able to develop a
civilization and advance culture and technology. |
|
11 |
CS11,1: Ability to manage several
streams of consciousness. |

This work is licenced under a Creative Commons Licence.