
Home |
Levels |
CQS |
Rating |
FAQ |
Papers |
Code |
Blog |
Calc (v3.Eng.Generic) |
Calc (v3.Eng.FPS) |
ConsScale is a scale used to rate the level of cognitive development of a creature
as a measure of key cognitive skills integration (cognitive functions sinergy).
The scale is based on the hypothesis that effective integration of these cognitive abilities (CSi,j) and associated
architectural components (AC) is required in order to develop behaviors associated with conscious beings.
There are two approaches to classify agents using the scale:
1. ConsScale Standard Evaluation Process:
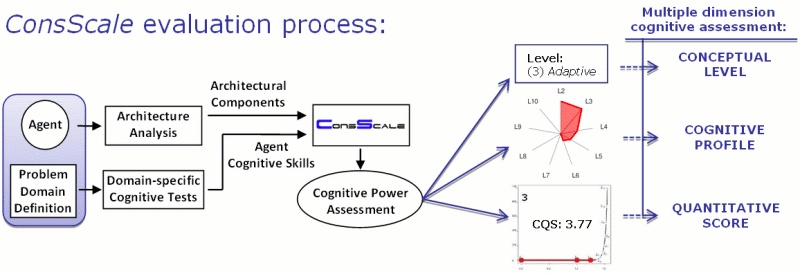
This process is oriented to existing implemented agents and provides an accurate and compelling measure of the level of cognitive development. However, it takes much more time and effort to be performed.
First of all, we need the actual agent and a particular problem domain definition for testing. As mentioned above, rating is based on architectural components and cognitive skills. Architectural components of the agent are identified through internal inspection of the implementation. Cognitive skills present in the agent are assessed thanks to the definition and execution of specific cognitive tests adapted to the established problem domain. Once we have the list of architectural components and cognitive skills found in the agent, we can apply ConsScale metrics to obtain the nominal level of consciousness, the cognitive graphical profile and the CQS score (you can use the Online Generic ConsScale Calculator to do this).
Note that comprehensive cognitive test/s have to be devised for each cognitive skill. These tests have to be designed in such a way that they validate the integrative and developmental inspiration of the scale. In other words, whenever possible, higher level cognitive tests will require the presence of all (or most) lower cognitive abilities in order to be passed.
See this paper for an example of the ConsScale Standard Evaluation Process in the domain of video game bots.
2. ConsScale Simplified Rating Process:
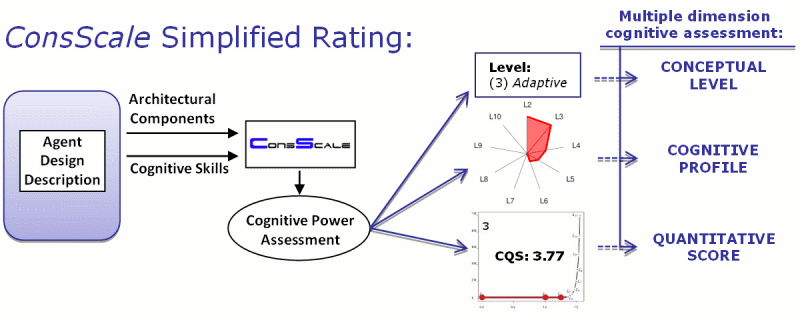
This rating process provides a quick approximation of the potential level of cognitive development of either an existing agent or even a computational model not yet implemented. The main benefit of this procedure is that a rating can be done within seconds simply using the ConsScale Calculator.
The ConsScale Simplified Rating process assumes the presence of architectural components and cognitive skills just by looking at the design blueprints of the system. Therefore, there is no need to perform any test or any domain-specific instantiation of the scale.
Of course, the rating obtained following this procedure is not accurate and can be considered just a vast approximation (and probably too optimistic). In the case of implemented agents, the Standard Evaluation Process should be performed in order to obtain a more accurate and realistic measure. However, the simplified rating provides a conceptual tool to evaluate the potential ConsScale level of a cognitive architecture even at design time, before any implementation of the model exists.
See below for some Simplified Rating examples.
|
|
Comparison between Standard and Simplified Rating Methods
|
|
|
Standard Rating
|
Simplified Rating
|
|
Applicability
|
Only existing implementations
|
Models, architectures, designs, implementations
|
|
Accuracy
|
High (realistic metric)
|
Low (potential, optimistic metric)
|
|
Cost
|
High (internal inspection of the implementation, cognitive tests design and execution)
|
Low (architectural components and cognitive skills are inferred directly)
|
|
CQS Computation Time
|
Within milliseconds
|
Within milliseconds
|
|
Problem Domain
|
Domain-dependent*
|
Domain-independent
|
|
Required Resources
|
Suitable testing environment, test procedures and associated tools, data collection / inspection / observation tools
|
Detailed description of the system
|
|
Output
|
ConsScale Level, Cognitive Profile, Quantitative Score
|
ConsScale Level, Cognitive Profile, Quantitative Score
|
|
Online Resources
|
ConsScale Calculator
|
ConsScale Calculator
|
|
* Actual cognitive tests are of necessity domain-dependent. They have to be performed in particular frameworks and real settings. Even the Turing test (level 10), is domain-dependent. Some authors have argued that Turing test is general-purpose, but is indeed specific to the domain of human accurate verbal interaction.
|
|
|
|
|
Notes:
- Simplified rating provides just an approximation of what could be the real ConsScale level of an implementation.
- Implementations (where available) should be rated using the ConsScale Standard Rating process (as described above) in order to obtain a more accurate and realistic measure.
- The rating obtained for models which have not yet been fully implemented, will have to be confirmed in the future by the application of the Standard Rating process to the corresponding implementations.
- For implementations or models which consider a developmental period, the rating considers the potential final ConsScale that they would achieve at the end of their developmental period.
|
| Name of system: | ELIZA |
| Description: | One of the first chatterbots (Joseph Weithenbaum, 1966). |
| Architectural Components: | B, Sext, A, R, M (see here for a description) |
| Cognitive Skills: | CS2,1; CS4,1; CS4,2; CS4,3; CS9,3 (see here for a description) |
| Radar Graph: | 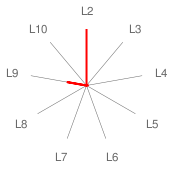 |
| CQS Graph: | 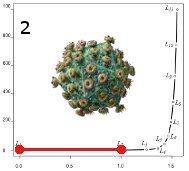 |
| CQS Value: | 0.18 |
| ConsScale Level: | LEVEL 2. REACTIVE. |
| Comments: | ELIZA is basically a reactive agent designed to detect and select keywords in the input and, using a script and pattern matching techniques, provide a response in the form of accurate verbal report (CS9,3). Although this agent presents one of the highest level cognitive skills (CS9,3), the final CQS is really low because ConsScale primes a developmental integration of cognitive abilities. In this particular case, it doesn't matter how good is the agent at producing well-formed linguistic reports; if the "mental" content reported is not created by a suitable combination of lower level cognitive abilities, the agent cannot be considered cognitively advanced.
|
| Name of implementation: | CERA-CRANIUM UT2004 Adaptive-Bot v3.4. |
| Description: | Unreal Tournament 2004 autonomous bot implemented using the CERA-CRANIUM cognitive architecture (Raśl Arrabales, 2009). |
| Architectural Components: | B, Sproprio, Sext, A, R, M (see here for a description) |
| Cognitive Skills: | CS2,1; CS3,1; CS3,2; CS4,1; CS4,2; CS4,3; CS4,4; CS4,5; CS4,10; CS5,2; CS5,4 (see here for a description) |
| Radar Graph: | 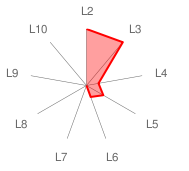 |
| CQS Graph: |  |
| CQS Value: | 2.69 |
| ConsScale Level: | LEVEL 3. ADAPTIVE. |
| Comments: | Although the implementation complies with some features of levels 4 and 5 it is rated as level 3. ConsScale requires the fulfilment of all cognitive skills of level i and also all lower levels in order to qualify as level i.
CQS for a pure level 3 agent is 2.22. The score of this agent (2.69) indicates that some additional features are in place. However, it is far from a level 4 agent who will score 12.21 or more. This can also be noticed in the radar graph, as L4 axis has a short spike (while L2 and L3 axes display full length lines).
|
| Name of implementation: | Minimal Architecture for Functional Imagination on CRONOS/SIMNOS |
| Description: | Implementation of a functional imagination mechanism that allows an embodied agent to simulate its own actions and their sensory consequences internally, and to extract behavioural benefits from doing so (Hugo Gravato Marques and Owen Holland, 2009). |
| Architectural Components: | B, Sproprio, Sext, A, R, M, Att (see here for a description) |
| Cognitive Skills: | CS2,1; CS3,1; CS3,2; CS4,1; CS4,2; CS4,3; CS4,4; CS4,5; CS4,6; CS4,7; CS4,8; CS4,9; CS4,10; CS7,6 (see here for a description) |
| Radar Graph: | 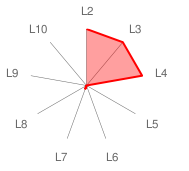 |
| CQS Graph: |  |
| CQS Value: | 12.24 |
| ConsScale Level: | LEVEL 4. ATTENTIONAL. |
| Comments: | The application of a minimal architecture for functional imagination (CS7,6) to CRONOS is rated as ConsScale level 4 (using Simplified Rating), however being a minimal architecture implementation, the proposal it is very promising in terms of achieving much higher scores (by adding level 5 set shifting capabilities).
|
| Name of model: | LIDA Model |
| Description: | The LIDA model is a (not yet fully implemented) comprehensive, conceptual, and computational model of cognition primarily based on the Global Workspace Theory (Franklin et al. 2007; Bernard Baars and Stan Franklin, 2009). |
| Architectural Components: | B, Sproprio, Sext, A, R, M, MN, Att, SsA (see here for a description) |
| Cognitive Skills: | CS2,1; CS3,1; CS3,2; CS4,1; CS4,2; CS4,3; CS4,4; CS4,5; CS4,6; CS4,7; CS4,8; CS4,9; CS4,10; CS5,1; CS5,2; CS5,3; CS5,4; CS5,5; CS6,1; CS6,2; CS6,3; CS6,4; CS6,5; CS7,6 (see here for a description) |
| Radar Graph: | 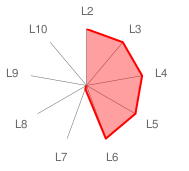 |
| CQS Graph: |  |
| CQS Value: | 101.36 |
| ConsScale Level: | LEVEL 6. EMOTIONAL. |
| Comments: | As in the case of Haikonen's architecture (below), a comprehensive testing of a full implementation of the LIDA model would be required in order to see if, for instance, the concept of self emerges in the ontology that the agent builds as part of its developmental period.
|
| Name of Architecture: | Haikonen's Cognitive Architecture |
| Description: | Cognitive architecture based on distributed signal representations and Haikonen Associative Neurons (Pentti Haikonen, 2007). |
| Architectural Components: | B, Sproprio, Sext, A, R, M, Att, MN, SsA (see here for a description) |
| Cognitive Skills: | CS2,1; CS3,1; CS3,2; CS4,1; CS4,2; CS4,3; CS4,4; CS4,5; CS4,6; CS4,7; CS4,8; CS4,9; CS4,10; CS5,1; CS5,2; CS5,3; CS5,4; CS5,5; CS6,1; CS6,2; CS6,3; CS6,4; CS6,5; CS7,1; CS7,2; CS7,3; CS7,4; CS9,3 (see here for a description) |
| Radar Graph: | 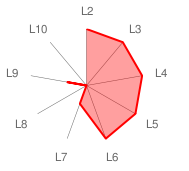 |
| CQS Graph: |  |
| CQS Value: | 114.16 |
| ConsScale Level: | LEVEL 6. EMOTIONAL. |
| Comments: | See Doan's article (page 5) on Haikonen's Cognitive Architecture for a discussion on its ConsScale rating. The implementation and testing of a Haikonen Machine would tell us if this architecture is even able to develop the models of self and other selves, thus promoting to ConsScale level 7 (Self-Conscious).
|

Raśl Arrabales. This work is licenced under a Creative Commons Licence.
|













